Build the Future
Encountering Building Information Building (BIM) for the first time whether as a student or a professional can be daunting. The team here at Cloudalize was no different. We too had to learn the BIM jargon, industry-specific phrases and acronyms.
That’s why we took the time to put together a BIM phrase book as a quick reference guide to BIM.

Cloudalize’s BIM phrase book is all you need to understand the terminology of Building Information Modelling (BIM).
BIM Phrase Book
Organised alphabetically, click the tabs to find more information.
Architectural Supplemental Information (ASI)
Architect’s Supplemental Instructions (ASI) are formal directions from an architect to resolve minor issues which may arise during a construction project. ASI advise how work should advance to resolve the issues concerned outside the contract signed between the contractor and the client. the ASI are included in any handover document prepared.
Big BIM
Big BIM defines the method by which the BIM methodology is applied across all levels of the project to each stakeholder. BIM values transparency, cooperation and real-time collaboration. Big BIM is the practical applications of BIM including: how to exchange information, how to manage the accessibility of data, how to collaborate remotely, etc.
Bill-of-Materials
A Bill-of-Materials (BoM) is a list of raw materials, components and parts needed for the manufacture of an end product or construction of a building. BoM helps the project stakeholders to plan raw material purchases and requirements. It provides foresight in estimating the cost of materials and, ultimately, reducing cost.
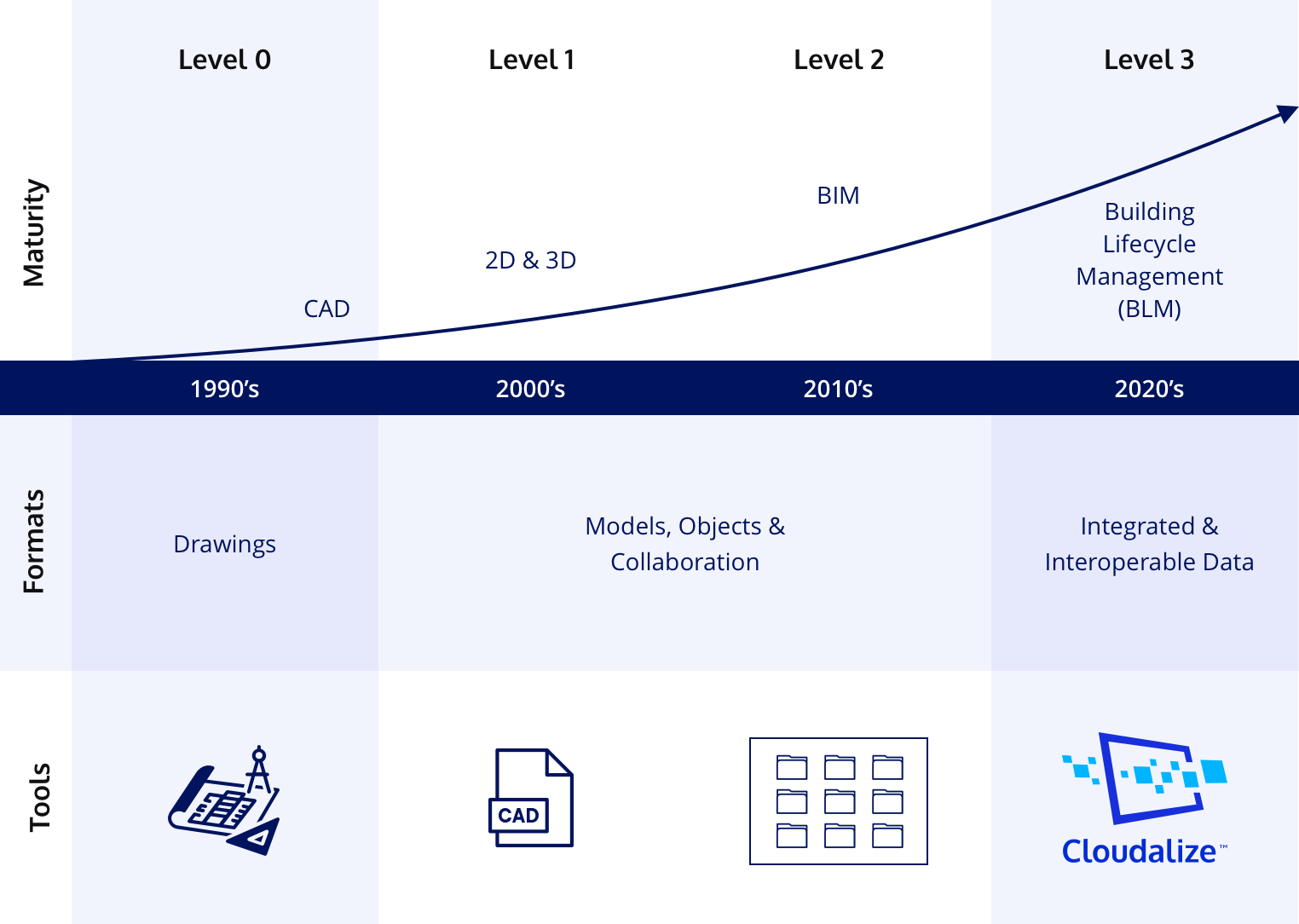
BIM Maturity Levels
The BIM Maturity Levels explain to which a company’s supply chain can operate and exchange information of the project with other stakeholders in the project life cycle. It started with Level 0 during the 1990s.
BIM-to-Field
BIM-to-Field is harnessing the accurate digital data contained within the 3D model and using it on-site for accurate and efficient operations, construction and maintenance.
Blueprint
A drawing containing information about a construction and its plan. Originally done by paper-and-pencil, Blueprints have evolved to be digital and 3D containing realistic visuals within the BIM framework.
Common Data Environment (CDE)
A Common Data Environment (CDE) is central repository of construction project information. It contains documents, graphical model and other project-related files.
Design-Bid-Build
Design-Bid-Build (DBB) is the traditional method of delivering a construction project from beginning to end. It remains the most widely used method and consists of three elements:
- The design phase;
- The tendering phase and;
- The construction phase.
It is still the preferred method because the project stakeholders will never have design surprises and it limits delays and changes and therefore the cost and schedule can be accurately predicted.
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)/Digital Terrain Model (DTM)
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM)/Digital Terrain Model (DTM) is a mathematical representation of the surface of the Earth in 3D. All buildings, vegetation and public services are removed from it to visualise just the terrain. DTM/DEM are obtained by surveying the area by a surveying drone and are used by civil engineers and geodetic engineers and are used in new modern constructions.
Digital Twin
A digital replica of the building. It can be created for buildings by using 3D BIM models
EU Directive 2014/24/EU
The European Union (EU) Directive 2014/24/EU on public procurement establishes the need for the use of data and digital tools (BIM) in the procurement process of construction work, services and supplies from September 2018. Directive 2014/24/EU is binding and must be implemented by EU member states.
Geographical Information Systems (GIS)
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) is software which manipulates, analyses and visualises geospatial information. GIS is a straightforward mapping tool however, the data can come from many sources and therefore is multilayered.
Geospatial
Geospatial is the collective name for a range of modern tools which help analyse location-based data and information. Accurate and reliable geospatial data is obtained from Global Satellite Navigations Systems (GNSS) equipment which track GNSS constellations such as GPS, QZSS, BeiBou, GALILEO and GLONASS. It is commonly used by surveying engineers when plotting the points of construction site.
Find out more about GNSS technology from the European Space Agency (ESA): ESA Navipedia
Isometric Drawing
Isometric Drawing or projection is a type of 3D drawing when the x, y and z axis are all at 120°. The advantage of isometric drawings is that the object can be freely oriented without redrawing it so the project stakeholders can visualise the entire building or object under construction.
Little BIM
Little BIM is defined as the setting up and implementing a BIM process within an organisation. Architects, engineers and construction professionals prefer to be familiar with BIM internally before engaging with BIM externally on-site or directly with a client. The first step is to make an informed choice about hardware and software and then advance managing the change within the organisation with personal, processes and workflows. Little BIM is a necessary condition for Big BIM.
Levels of Development (LoD)
Levels of Development (LoD) allows BIM project stakeholders to stay up-to-date with progress. It defines the information, data and linked documentation at different milestones of the project. Ultimately, it facilitates the BIM projects reliability.
Level of Accuracy (LoA)
For BIM, of Accuracy (LoA) is a reference which enables AEC professionals to articulate and benchmark to which level of predefined specifications. The intention to to provide a framework from which the project results can be benchmarked with the predefined specifications.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
Public-private partnerships (PPP) are when private-enterprise and the civil administration – i.e. government – work together to complete a project to provide public services. PPPs have been used to fund and construct infrastructure projects around the world including dykes, hospitals, public transport systems and bridges.
Point Cloud Survey
Point clouds are created by laser scanning an existing building to capture it in 3D. This data can be used to create an accurate and parametric 3D model of the building.
Request-for-Information (RfI)
Request-for-Information (RfI) is a document used to obtain information about a product, service and suppliers of a construction or manufacturing form. RfI are formal and are a preliminary document sent early in the process about a firm’s ability to meet specific needs and to solve unique issues that it has for its end product or building.
Request-for-Proposal (RfP)
A Request-for-Proposal (RfP) comes after a RfI. It is a formal document which details information from an external party to solicit bids to complete a project or a particular objective of the project. The RfP outlines the tendering process, contract terms and terms of reference. When a RfP is sent, it can be safely assumed that there are multiple parties to the tendering process.
Single-Source-of-Truth
A Single-Source-of-Truth is another term for Common Data Environment (CDE)
Statement-of-Work (SoW)
A Statement-of-Work (SoW) is used on-site of the project to detail the BIM project’s work requirements. It can outline the deliverables of the project, the scope of the project, the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) as well. It is useful for project and contract management as it outlines the liabilities, agreements and division of responsibilities between the client and the contractors.
Smart City
A smart city is an urban area where Internet-of-Things (IoT) is deployed to gain insights for the benefits of the whole community. A smart city relies on modern and digital solutions to improve life for goals and optimise services for the commercial sector. The end goal is efficient delivery of public services, responsive municipal authorities, safer streets and meeting the needs of the population into the future.
Virtual Design Construction
Developed by the Engineering Facility at Stanford University, Virtual Design Construction is not an additional BIM level. VDC is a combination of new and available technology – including BIM – with additions of planning and development tools. BIM models are used to create digital twins of the building to plan and construct digitally before any physical work is done. VDC also uses project and portfolio management tools to calculate costs, evaluate risks and estimate sustainability.
